EXPERT INSIGHT
Maximizing Efficiency and Minimizing Costs: The Benefits of Preoperative Planning in ASCs
In recent years, ambulatory surgery centers (ASCs) have become increasingly popular for patients requiring hip or knee replacement as these facilities provide more convenient and same-day surgical care while also offering surgeons the opportunity to perform joint replacement procedures in a more cost-efficient manner. However, the surgery must be well-prepared to successfully streamline joint arthroplasty. Everything needs to be predictable.
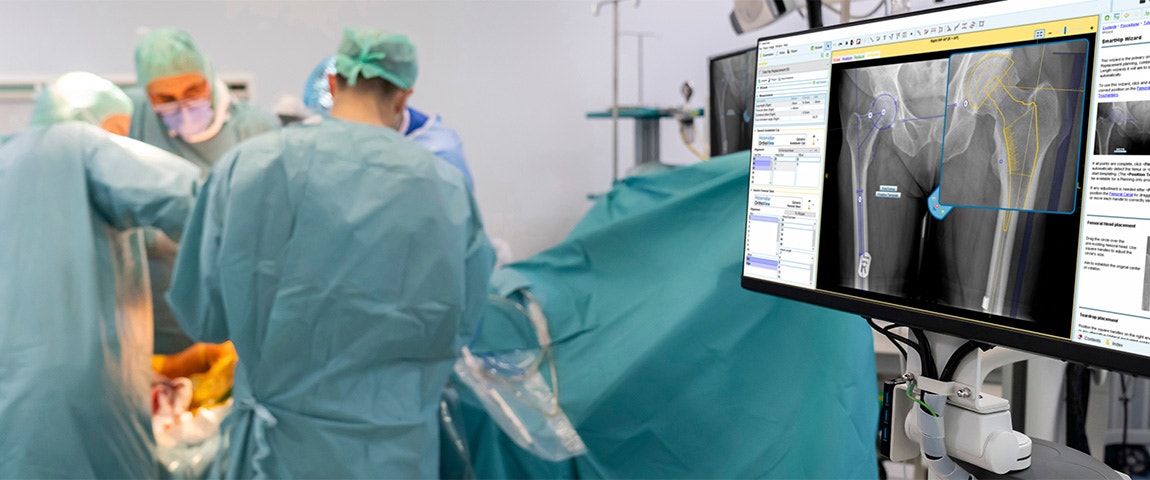
This is where X-ray preoperative planning, also known as digital templating, comes into play. Preoperative planning involves carefully considering all aspects of a surgical procedure before it is performed. This includes identifying any potential risks or complications, selecting the appropriate equipment and instruments, and preparing the patient for surgery. By planning ahead, surgeons can ensure that each procedure is performed safely and effectively and that patients receive the best possible outcome [1].
This article presents evidence that digital preoperative X-ray templating benefits ASCs, patients, and orthopaedic surgeons by improving surgical outcomes, enhancing workflow efficiency, reducing costs, and minimizing resource needs.
Enhanced accuracy improves surgical outcomes
According to a recent study by Mahoney et al. [2], accurate preoperative planning can significantly improve surgical outcomes and reduce complications such as malalignment, impingement, and instability. They demonstrated that implant-related complications were significantly lower in the group that underwent hip replacement with prior x-ray-based preoperative planning (4%) compared to the group that underwent hip arthroplasty without preoperative planning (16%).
A study published by Röder et al. in the Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery found that the use of preoperative planning resulted in a 131% reduction in revision surgeries for total hip arthroplasty. He and his colleagues demonstrated this through a randomized controlled trial (RCT) on 257 subjects where the preoperative planning group had a significantly lower revision rate of 3.1% compared to an 8.1% revision rate in a group in which the implant size was determined intraoperatively without the use of digital templating [5]. Furthermore, they stated that preoperative planning can lead to improved implant longevity, function, patient satisfaction, and reduced revision rates [5].
More than a decade ago, orthopaedic departments demonstrated an agreement between preoperatively planned and implanted component sizes of 90% or more [3]. More recently, in 2019, Newman et al. demonstrated that state-of-the-art digital templating software was accurate within one size in 97% (344 of 354) primary hip cases [4]. Accurate positioning of a calibration marker by radiographers is paramount for achieving such levels of accuracy.
Minimizing operating time to save money
In addition to improving surgical outcomes, preoperative planning can enhance workflow efficiency, especially in ASCs. With digital templating, surgeons can have a clear plan in place before the surgery, which enables them to make precise and efficient decisions during the surgery. This can minimize the need for intraoperative adjustments, improvisations, or delays. Preoperative planning can also facilitate communication between the surgeon, the patient, and other healthcare providers, which can help ensure a smooth and effective surgical experience.
A study conducted by Meermans et al. on 163 subjects demonstrated that operative time was significantly reduced by 13% in a group who underwent digital templating) compared to a group that did not. [6]. This not only saves time but also reduces costs associated with surgery.
Significant cost savings by reducing instrumentation
Preoperative planning can also benefit ASCs by reducing the need for additional resources. By accurately predicting implant sizes and placement beforehand, surgeons can minimize the requirement for extra instruments and implants, resulting in cost savings for ASCs.
Research studies have shown that digital templating software significantly reduces the number of instrument trays required during surgery. In a study conducted by Levine et al.[7], the use of digital templating software reduced the number of instrument trays to an average of three in 97% of knee replacements (n=82), compared to non-templated TKAs, which required 6-9 trays.
Based on standard fees to sterilize and package implant trays (approximately $26 based on a survey of 10 orthopaedic hospitals performing TKA), Levine and colleagues estimated almost $10 000 of cost-saving by using template-directed instrumentation over the 1-year study period [7].
Another study by Röder et al. showed that preoperative planning significantly lowers hospitalization costs by 18% [5]. The authors concluded that determining the optimal implant size before surgery based on radiographic templating leads to a lower revision rate, shorter hospital stay, and lower overall costs. They recommend routinely using preoperative planning in total hip arthroplasty to improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs.
These cost reductions related to optimized instrumentations and hospitalization lead to significant cumulative savings for ASCs, ultimately benefiting patients and providers.
In conclusion, preoperative planning through X-ray templating software can provide significant benefits for ambulatory surgery centers, their patients, and orthopaedic surgeons. Accurate preoperative planning can lead to improved surgical outcomes, enhanced workflow efficiency, reduced costs, and minimized need for additional resources. As such, ASCs should consider implementing preoperative planning as a standard practice to ensure the best possible outcomes for their patients and optimize the value of care.
L-103400
- Schlosser TP, Fornari ED. Preoperative planning in orthopaedic surgery. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2008;16(10): 555-67. doi: 10.5435/00124635-200810000-00002]
- Mahoney, O. M., Kinsey, T., & Mont, M. A. (2010). X-ray-based planning for total hip arthroplasty reduces implant-related complications and reoperations. The Journal of Arthroplasty, 25(4), 590-594
- Eggli S, Pisan M, Muller ME. The value of preoperative planning for total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg 1998 80-B: 382-390.
- Newman M, Shaw G, Kane T. Assessment of an Orthopaedic Templating Software Package for Cemented Total Hip Arthroplasty The Journal of Hip Surgery 2019; 03(02): 059-061
- Röder, C., Staub, L. P., Dietrich, D., Eggli, S., Busato, A., & Müller, U. (2012). Economic and clinical benefits of preoperative determination of the optimal implant size in total hip arthroplasty. The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery, 94(4), e26.
- Meermans, G., Malik, A., Witt, J., & Haddad, F. S. (2012). Preoperative radiographic templating reduces operative time in total hip arthroplasty. The Journal of Arthroplasty, 27(8), 1500-1505.
- Levine BR, Hsu AR, Gross ChE, Bhatia S. Template-directed Instrumentation in Total Knee Arthroplasty: Cost Saving Analysis. Orthopedics. 2012;35(11) e1596-e1600
Share on:
You might also like
Never miss a story like this. Get curated content delivered straight to your inbox.