TRENDS
3D Printing at the Point of Care — Navigating the Trends of 2024
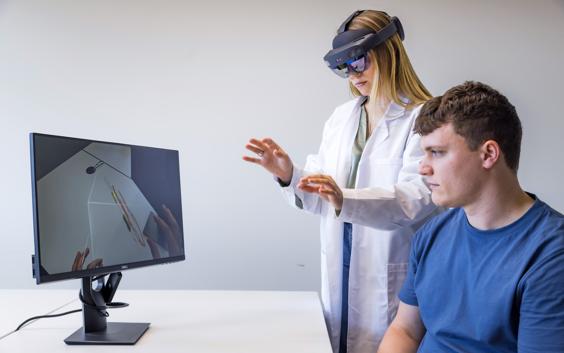
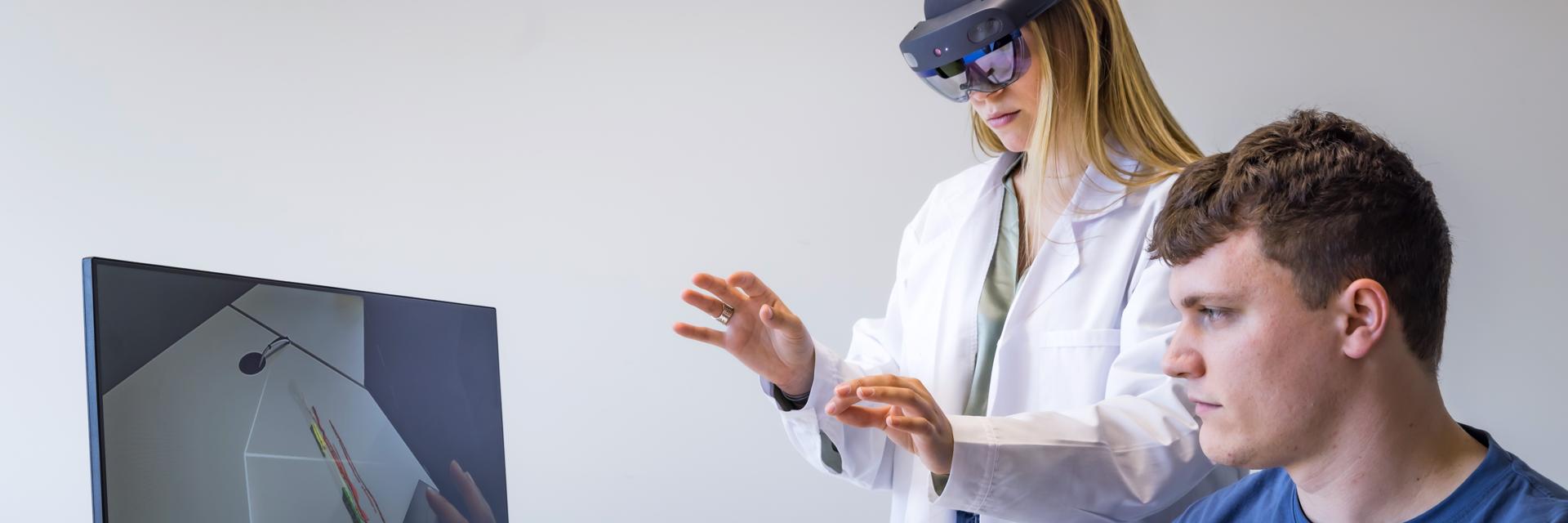
In the dynamic landscape of healthcare, 3D printing at the point of care continues its groundbreaking journey, pushing the boundaries of what's achievable in modern medicine. As we venture into 2024, a set of pivotal trends is steering the course of 3D printing technology, offering unparalleled prospects in automation, diverse applications, cloud integration, quality assurance, and heightened accessibility.
Automation takes center stage
Automation stands out as the backbone of the ever-evolving world of 3D printing workflows. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) segmentation is surging, revolutionizing processes across clinical specialties such as cranio-maxillofacial (CMF), cardiovascular, and orthopaedics. Materialise leads the charge with an extensive medical device software portfolio for AI-enabled segmentation, now including ankle and torso in its catalog.
Beyond segmentation, automation plays a pivotal role in enhancing workflow efficiency. Tools like Materialise Mimics Enlight CMF are transforming virtual surgical planning for complex surgeries like orthognathic and reconstruction. This automation surge not only improves efficiency but also elevates the precision and accuracy of 3D-printed medical models and devices, like occlusion splints.
Expanding applications
Gone are the days when anatomical models were innovative features. The 3D printing landscape is experiencing an explosion of applications, overstepping traditional boundaries. While clinical specialties like CMF and orthopaedics continue to benefit, the spotlight has now broadened, with surgical guides becoming increasingly more prevalent. In cardiology, as seen at the World Congress of Pediatric Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery, the pivotal role of 3D planning and printing, often paired with virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), takes center stage. Oncology is also advancing, with applications ranging from surgical guides to visualizing complex tumors and pioneering 3D-printed radiotherapy devices, like boluses, brachytherapy applicators, or aperture blank accessories.

Embracing the cloud
Cloud technology adoption is rapidly gaining momentum, despite initial security concerns. Hospitals globally recognize a multitude of benefits, from data loss prevention to improved collaboration and access to cutting-edge AI tools. Cloud integration streamlines workflows, enhancing the overall efficiency of 3D printing processes.
Quality assurance remains paramount
Quality remains a focal point for 3D printing at the point of care. Strict regulatory requirements, particularly in Europe due to the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), push hospitals worldwide to uphold the highest standards. In this context, ensuring traceability is imperative, with case management playing a pivotal role. Materialise introduced Materialise Mimics Flow Case Management, a tailored platform for 3D printing labs at the point of care that fosters collaboration and supports quality management systems (QMS).
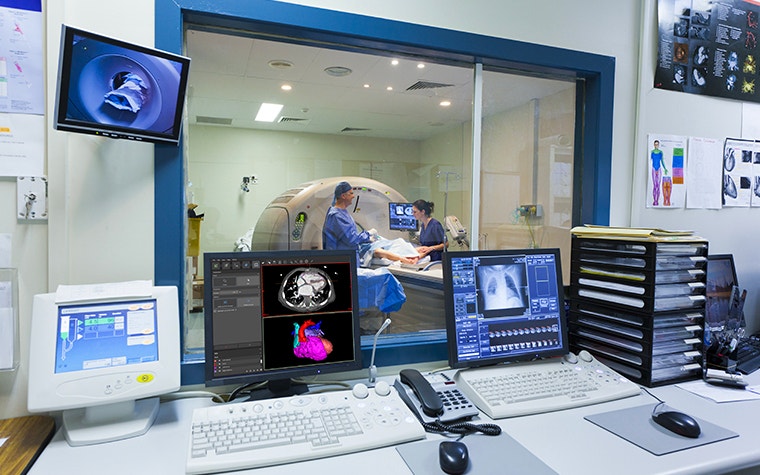

Increasing accessibility
An increasing number of hospitals are embracing 3D printing in-house as the technology becomes more accessible. The decreasing cost of 3D printers, coupled with user-friendly automation-driven software, makes the technology more approachable. Collaborative initiatives, such as the partnership between Materialise and RICOH, pave the way for smaller hospitals to harness the power of 3D printing, expanding its reach across the healthcare spectrum.
Entering a transformative era
The trends of 2024 indicate a transformative era for 3D printing at the point of care, where automation, diverse applications, cloud integration, quality assurance, and heightened accessibility converge to redefine the future of healthcare. As these trends unfold, the potential for innovative solutions and improved patient outcomes through 3D printing technology remains limitless.
L-103856-01
Share on:
You might also like
Never miss a story like this. Get curated content delivered straight to your inbox.
