CASE STUDY
Young Girl Can Breathe Easy Thanks to Materialise Mimics
Case presented by W. Vos, J. De Backer, P. Germonpré, P. Parizel, F. Wuyts, and W. De Backer (Departments of Pulmonology, University Hospital Antwerp; Radiology and ENT, Department of Physics, Antwerp, Belgium; University of Antwerp, Antwerp, Belgium)
The challenge
Develop a treatment plan for a patient with decreased lung capacity
Kyphoscoliosis, a deformation of the spine that consists of both lateral and posterior curvatures, often results in decreased lung capacity in those who suffer from it. This was the case of a 16-year-old female patient. She had been wearing an orthopaedic corset to control her spinal deformation; however, when she stopped wearing it at the age of 16, a wheezing sound developed.
Dr. Vos and his team wanted to gain insight into the patient’s medical condition and develop a custom treatment plan that would enhance her overall quality of life.
The solution
Functional respiratory imaging using Mimics and a personalized stent
To assess the patient’s problem and reach a diagnosis, Dr. Vos and his team turned to advanced functional respiratory imaging, using Materialise Mimics and flow simulations. The first step was a classic lung function test to determine the patient’s total lung capacity. Results revealed it to be only 57% of the normal level for a girl her age and height.
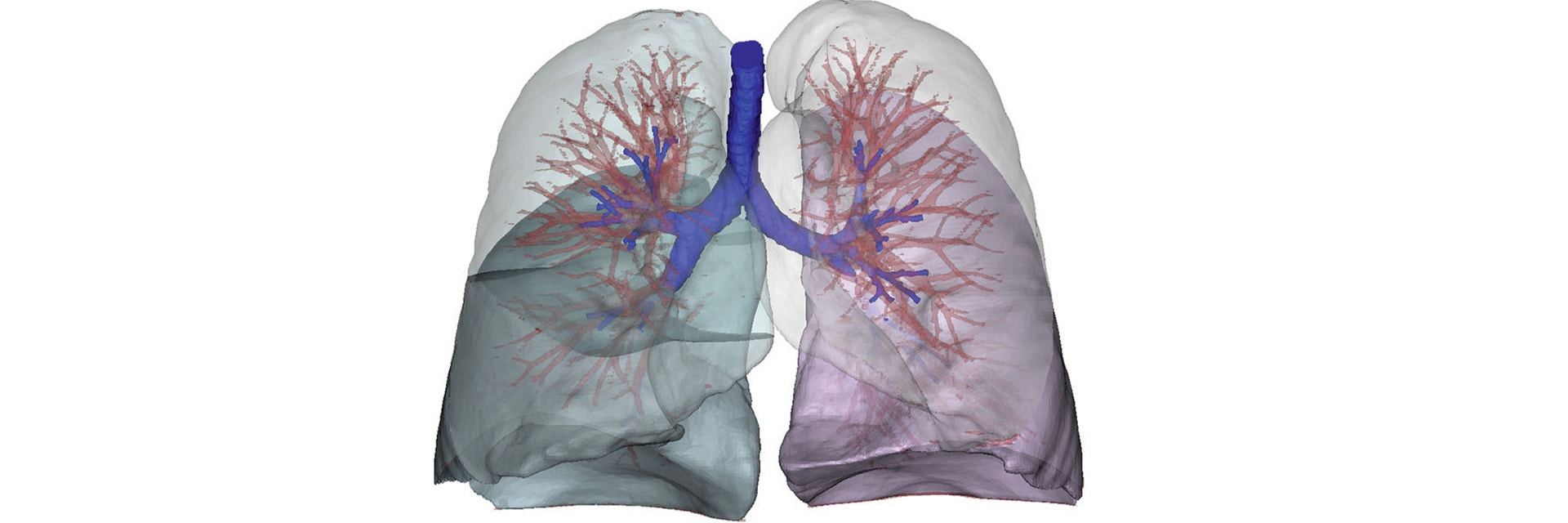
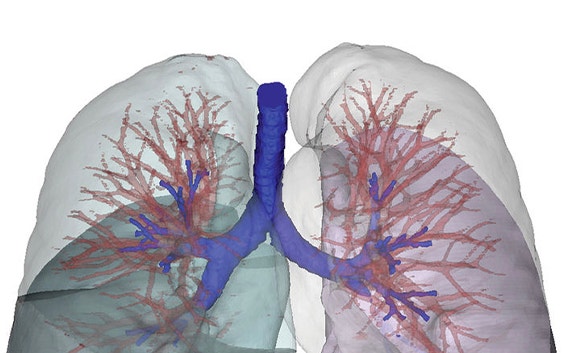
Next, to determine the origin of the wheezing sound, a CT scan was taken while the lungs were at full capacity. The CT data was then imported into Mimics for easy visualization of the spine and its deformation, the lung lobes, and the airway tree. The image showed a drastically smaller right lower lobe and a malformation and occlusion of the airway tree in the right lung. The extremely small lower lobe, in combination with the occluded airways, was considered to be partly responsible for the wheezing sound.
“It can be said that innovative advanced functional imaging using Mimics and flow simulations can improve the level of healthcare in the field of pulmonology through patient-specific analyses.”
— Dr. Vos et al, University Hospital Antwerp/University of Antwerp, Belgium
Before the patient stopped using her corset, the pressure of the corset, combined with her spinal curvature, had caused a total collapse of the airway entering the right lower lobe, preventing any air from reaching this region. After removing the corset, the pressure on the right lobe disappeared, allowing it to become ventilated at high lung volumes. The small bronchial diameter at the level of the truncus intermedius and the high-mass flow rates at larger lung volumes led to a high-velocity flow in this bronchus, which in turn caused the wheezing.
Based on their findings, the researchers suggested a patient-specific treatment plan to overcome the underlying cause of the wheezing and allow air to reach the right lower lobe during the complete breathing cycle, not just at high lung volumes.
To that end, they designed a stent to open the airway tree. They carefully calculated the stent’s dimensions and placement based on 3D models and data generated with Mimics’ accurate visualization and measurement tools. The data and 3D models were further used for surgical simulation, which allowed for a better understanding of the anatomy ahead of the surgery.
Using Mimics for functional respiratory imaging in combination with computational fluid dynamics, the researchers were able to accurately predict the outcome of the treatment, i.e. its effect on the patient’s lung capacity.
“It can be said that innovative advanced functional imaging using Mimics and flow simulations can improve the level of healthcare in the field of pulmonology through patient-specific analyses. The versatility of the technique and the positive outcomes when used in a clinical setting strengthens the belief that functional imaging using Mimics and CFD can become a standard tool in pulmonology worldwide.” Dr. Vos et al, University Hospital Antwerp/University of Antwerp, Belgium
The result
Lung capacity increased from 57% to 68% and wheezing was eliminated
Seven months after the placement of the stent, the results were promising, with total lung capacity increasing from 57% to 68%. It was anticipated that within 18 months the patient’s lung capacity would approach normal levels.
Even if the patient’s congenital medical condition prevents her total lung capacity from ever fully achieving normal values, the treatment successfully dealt with the patient’s initial complaint, as the wheezing sound disappeared immediately after the stent was put in place.
In addition to successfully treating their patient, the researchers also achieved the goals they set before the start of the study — to perform a patient-specific evaluation, suggest an appropriate therapy, and predict the outcome using advanced functional imaging techniques.
The researchers believe that these techniques will become standard tools in pulmonology, increasing each patient’s quality of life and decreasing their share of overall healthcare costs.
This study earned Dr. Vos et al. a Mimics Innovation Award, which celebrates cutting-edge work by early-stage researchers using Materialise software to advance personalization in healthcare.
L-102835-02
Share on:
This case study in a few words
Healthcare
Mimics
Enhanced spatial insights
Personalized device design
Preoperative planning
Surgical simulation